Abfraction is a type of non-carious (decay) lesion at the cemento-enamel junction.
This is a chronic problem that can lead to gradual tooth loss. And the problem is that it can be asymptomatic. So, you may not even realise you have it until it is significantly worsened.
The exact causes of abfraction are unclear, but some “chemical, biological and behavioural” factors are thought to be responsible, according to research published in Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.
Knowing and understanding this condition can be important in getting early treatment and preventing its progression.
What Is An Abfraction?
Abfraction means “to break away.”
The term’s derived from the Latin words “ab,” meaning “away,” and “fraction,” meaning “to break,” by John O. Grippo – the first to name these lesions in his research titled “ Abfractions: A New Classification of Hard Tissue Lesions of Teeth.”
He theorised that these wedge-shaped dents were a result of “biomechanical loading forces” (originating from swallowing, chewing, and clenching).
And the severity of these lesions depended on the magnitude, duration, direction, frequency, and location of the forces.
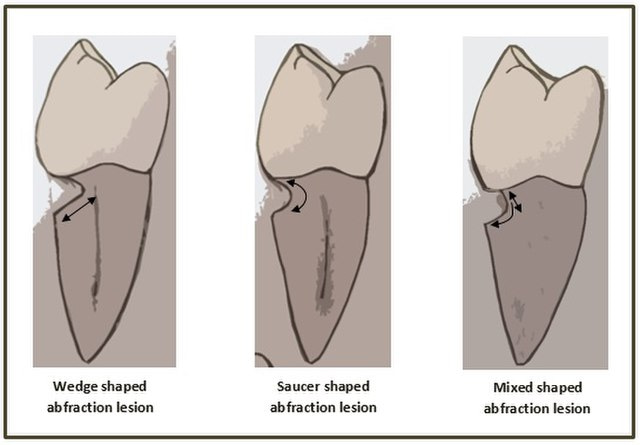
There is chipping of enamel and dentin near the gumline. And a single tooth can have more than one abfraction lesion.
In most cases, these develop on the front teeth (with a higher risk on the lower jaw) and on the premolars (between the canines and back teeth).
What Are The Characteristics Of Tooth Abfraction?
Tooth abfractions appear as “U” or “V”-shaped dents below the gum line, with sharp internal and external borders.
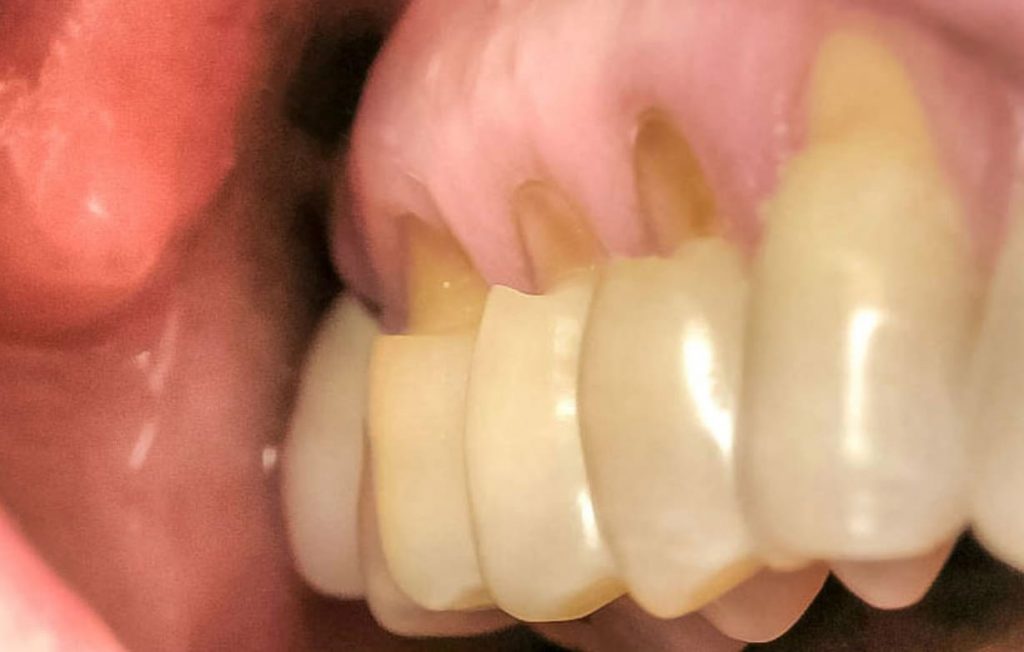
Usually, dents with sharp edges are caused by excessive force, according to a study published in Inside Dentistry. There are, however, times when these lesions are “concave,” indicating “toothpaste abrasion” as the primary cause.
These lesions can also be accompanied by:
- Wear facets (shiny, polished tooth surface, which can indicate compressive occlusal forces)
- Chipped tooth
- Gum recession
- Tooth decay
- Loose tooth
Eventually, it can also result in the loss of a tooth.
It should also be noted that abfractions can be asymptomatic as well. You might not notice anything different with your teeth.
While in its earlier stages, abfraction can cause some temporary sensitivity, according to the study published in Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.
However, since the dentin counterheals, it can simply go away. So, again, you might not know what’s happening until it’s become more prominent.
What Causes Tooth Abfraction?
Tooth abfraction is likely caused by excessive occlusal forces, toothbrush/toothpaste abrasion and/or acid erosion.
It’s believed that the hydroxyapatite crystals in the enamel and dentin wear away due to occlusal forces.
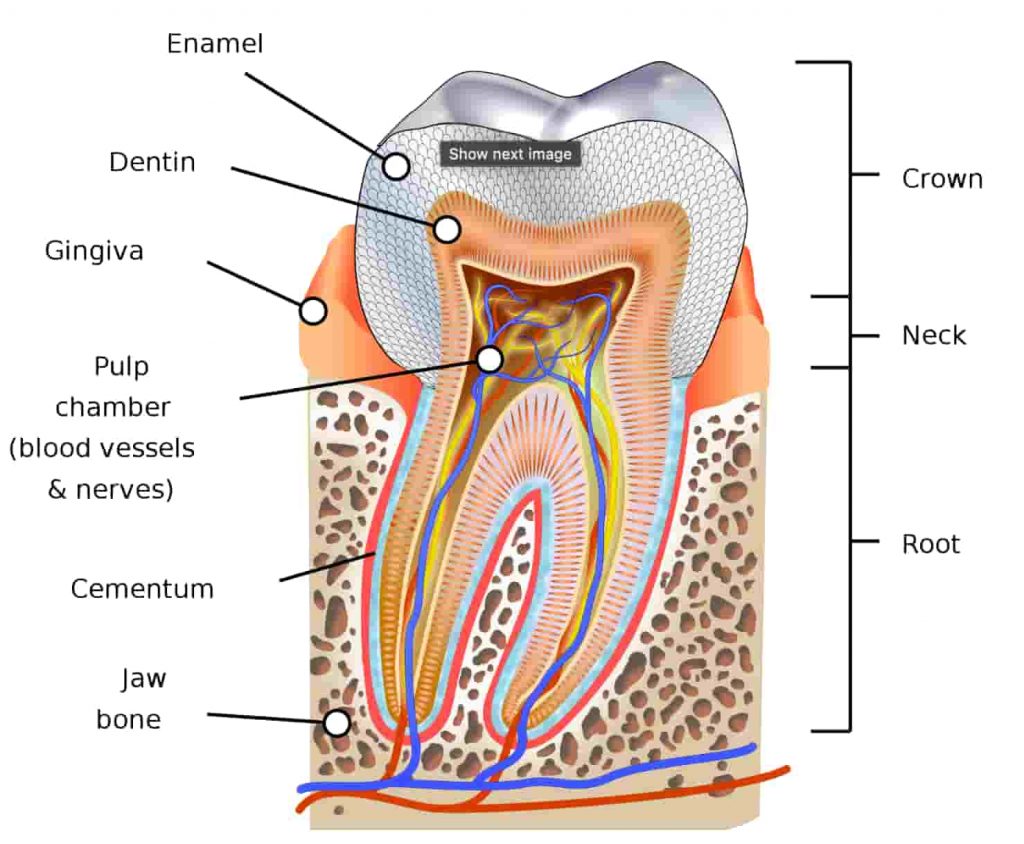
This is exacerbated by the thinness of the enamel near the neck (or cervical area) of the tooth.
The low packing density of the Hunter-Schreger Band (a part of the enamel) at the cervical area is also thought to contribute, according to research published in the Journal of Anatomy.
These occlusal forces can come from:
- Chewing
- Teeth grinding (bruxism)
- Parafunctional habits (nail biting, thumb sucking)
- Malocclusion
Apparently, they cause tooth flexure, which ends up damaging the enamel.
Still, excessive force and tooth anatomy are not the only causes.
It’s widely believed that external factors, such as acid exposure (from foods and illnesses like GERD and eating disorders), the abrasiveness of the toothpaste and even the brushing technique may be responsible (although not primarily) for the development of abfractions.
Despite this, it is still unclear what initiates and/or causes the lesions. For instance, research has shown that not everyone with bruxism ends up with abfractions.
For these and many other reasons, it’s thought to be multifactorial.
How Common Are Tooth Abfractions?
One review published in the Journal of Dentistry reported that tooth abfractions had a prevalence rate of 27% to 85%.
Although research shows that its incidence increases with age. It increases from 3% to 17% between the ages of 20 and 70, according to the review published in Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.
Is An Abfraction Serious?
Abfraction lesions result in the loss of tooth structure, which can cause serious oral health problems.
Aside from cosmetic problems, together with erosion and abrasion, it can even lead to tooth loss. Additionally, it can affect the tooth root and surrounding gum tissue.
Therefore, it’s important to get it treated.
How To Treat Abfraction?
Different treatment options for abfractions include:
- Tooth fillings
- Night guard
- Occlusal splints
- Dental crowns and veneers
- Braces, aligners, or retainers
Your treatment plan will be determined by the severity of the problem and the symptoms you are experiencing.
Keep in mind that abfractions are caused by a variety of factors. So, they’ll have to be identified first.
Orthodontic treatment may be recommended, for example, if your teeth are misaligned. In this way, certain teeth will be subjected to less pressure.
If the problem is parafunctional habits, you might have to undergo behaviour therapy. You might also be recommended a different brushing technique to prevent further damage.
Similarly, if you have a habit of grinding or clenching your teeth, you might be given a night guard to wear.
As far as repair work is concerned, a dentist might consider filling the lesion if it extends deep into the gums. Root coverage or gum grafting procedures might also be recommended.
Other than that, dental restorations are also popular for fixing abfractions. Only the problem is that there’s a high chance of them failing.
Additionally, restorations won’t stop abfractions from progressing further.
Still, they can be helpful if the patient wants to hide them for cosmetic reasons. They can also be considered if the underlying tooth has become too weak and sensitive.
Does Abfraction Need To Be Treated?
Not all abfractions require treatment. In the case of minor dents that aren’t causing any serious problems, they can be left as is.
Still, it’s extremely important to monitor them for any change. And for that, you must get regular checkups.
If at any point you feel pain, sensitivity, or anything unusual, you should contact your dentist.
Conclusion
Dental abfractions can pose serious oral health problems since they chip away at the tooth structure.
They can keep worsening over time while causing permanent damage. Therefore, if you notice any unusual dents along the gum line, you should have your teeth checked.
There are treatments that can prevent the further progression of these lesions. However, they can be caused by a combination of factors, it’s important to consult an experienced, board-certified dentist.
Reviewed and Approved by Dr Izbel Aksit
FAQ
What is abfraction vs erosion?
Abfraction and erosion are both types of tooth wear. The difference between erosion and abfraction is that erosion is caused by acid in food, drinks, vomit, or reflux, while abfraction is caused by excessive occlusal force, abrasion, and acid exposure.
What is abfraction vs attrition?
Both abfraction and attrition cause the loss of tooth surface. In attrition, this occurs due to tooth-to-tooth contact (due to bruxism, for instance). And in abfraction, it’s due to occlusal forces, friction from abrasive objects and acids. Attrition is characterised by smooth and shiny wear facets, while abfraction by its wedge-shaped notches.
What is abfraction vs abrasion?
Both abrasion and abfraction are types of non-caries damage to teeth. Abrasion results from friction between the teeth and foreign objects. Abfraction results from tooth flexure due to excessive forces, abrasive foreign objects, and acids.
Do dental abfractions heal?
Abfractions are unlikely to heal. Keep in mind that they can cause permanent loss of tooth structure, which is why you shouldn’t delay treatment.
Can tooth abfractions be fixed?
It’s possible to fix dental abfractions with fillings, night guards, splints, orthodontics, and restorations. Depending on the severity of your problem, surgery might also be required.
Are dental abfractions normal?
The presence of dental abfractions isn’t normal since they may indicate excessive pressure on teeth and harmful exposure to abrasive substances and acids. So, you need to get them checked by a dentist.