An itchy tongue can cause quite some discomfort. Depending on the underlying cause of the problem, it can also be accompanied by other more painful and even dangerous symptoms.
While there are different reasons why your tongue might be itching, you must get it checked as soon as possible because it can be one of the early signs of anaphylaxis or anaphylactic shock, which is a serious and potentially fatal allergic reaction.
In this guide, you’ll learn more about the different causes of an itchy tongue, the different symptoms that might accompany it, and what you can do to get relief from this problem.
Why Is My Tongue Itchy?
Some of the reasons why your tongue might feel itchy are as follows:
Oral Allergy Syndrome (OAS)
Oral allergy syndrome, also known as pollen-food allergy syndrome, is a type of allergic reaction. According to Allergy UK, it can be triggered by the eating of raw fruits, nuts and vegetables, affecting:
- Those with hay fever (allergic rhinitis)
- Those sensitive to “airborne pollen from trees, grasses or weeds,” birch tree pollen being the most common culprit.
Certain proteins in these fruits, nuts and vegetables are mistaken for pollen by the allergy antibodies, as per NHS Inform. Furthermore, according to the Oxford University Hospitals (OUH) NHS Trust, the skin of the fruit and vegetable can cause an allergic reaction. While its risk is lowered when cooked, it can still happen. And even rubber latex has been implicated as a trigger of oral allergy syndrome.
As far as symptoms go, the OUH reports the following:
- In “common form” – red, itchy, swollen, and burning tongue, lips, inside of the mouth and soft palate.
- On occasion – itching and swelling of the throat which may later be accompanied by hives, conjunctivitis, rhinitis, asthma, nausea and vomiting.
- Rare – include severe symptoms like anaphylaxis or breathing difficulty.
Allergy UK reports that most people experience mild symptoms 5-10 minutes after contact with the allergen. Still, even if an anaphylactic shock is rare, if you do develop it, you must call the emergency services immediately as it can be fatal.
Angioedema
Angioedema refers to the swelling of a part of the body below the skin. According to the NHS, this condition is often the result of an allergic reaction and usually affects the tongue, lips and eyelids on the face, genitals, and hands or feet. There are other types of angioedema as well, such as hereditary angioedema, idiopathic (when the cause is not known) angioedema, drug-induced angioedema, etc.
While an itchy tongue can be one symptom of this condition, the MSD Manual also reports others, such as:
- Swollen hands or feet, eyelids, tongue, face, lips or genitals.
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Nausea, vomiting
- Hives
Moreover, they report that angioedema can cause swelling of the “membranes lining the mouth, throat, and airways,” an anaphylactic reaction, and “dangerously low” blood pressure. Angioedema can also be life-threatening, which is why you must get emergency help right away.
Burning Mouth Syndrome (BMS)
Burning mouth syndrome is another condition that can make the tongue itch. However, that’s not the only thing that your tongue might experience. As the name suggests, burning mouth syndrome makes it feel like the mouth is burning, and it can be painful. Other symptoms can include numbness, dry mouth and changes in the sensation of taste.

There are two types of burning mouth syndromes, according to the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR):
- Primary Burning Mouth Syndrome – when the cause is not known, but it’s believed to be a result of nerve damage.
- Secondary Burning Mouth Syndrome – when burning mouth syndrome may be the result of poor oral habits (like bruxism), depression, changes in hormones, allergies, xerostomia, nutritional issues, infection, acid reflux, and certain medications.
Since this condition can also cause a lot of discomfort, it’s important that you get in touch with your healthcare provider for a check-up.
Herpes Virus
Herpes simplex virus (both type 1 and 2) can result in the formation of tongue sores, which can, in turn, cause itchiness, among other symptoms. This is a very contagious condition and is acquired by coming into contact with someone who is also infected. It can be transmitted through things such as sharing objects like toothbrushes, utensils, lip balms, etc., bodily fluids, saliva, skin-to-skin contact, and sexual intimacy.

You may experience different symptoms depending on which stage of herpes you’re in. Cedars-Sinai has outlined it as follows:
- At first, itching, pain, redness, and heat along with swelling can be experienced in the area about to erupt.
- Fluid-filled blisters will appear, and they can cause pain.
- Blisters ooze and form sores
- Crust forms after 4-6 days, and the healing begins.
Oral Candidosis
Oral thrush is a fungal infection caused by Candida albicans. This condition can also leave your mouth itchy in addition to causing:
- Creamy white lesions form
- Bleeding on scraping the lesions
- Raised spots that resemble cottage-age in appearance
- Cracking and dryness of the corners of the mouth
- Loss of taste
- Soreness, burning and cottony feeling in the mouth
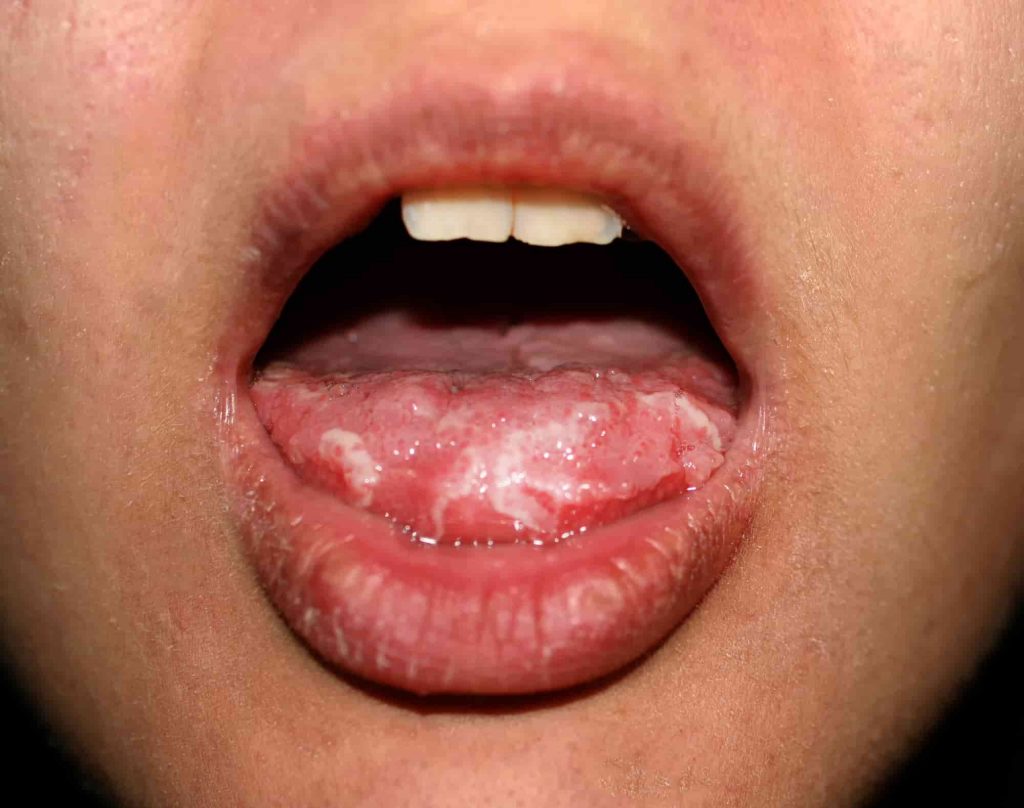
The condition can cause other symptoms as well, so it’s best if you get yourself checked by your doctor.
According to StatPearls, the condition develops secondary to the suppression of the immune system, which can happen as a result of extremes of age, such as a newly-born child or an old person, diseases like HIV/AIDS, and long-term use of steroids and antibiotics.
Xerostomia
Xerostomia or dry mouth can leave the tongue without moisture which can also make it feel itchy. Some of the other symptoms of this condition also include:
- Bad breath
- Difficulty chewing, talking, and swallowing
- Altered sense of taste
- Difficulty wearing dentures
- Tooth decay
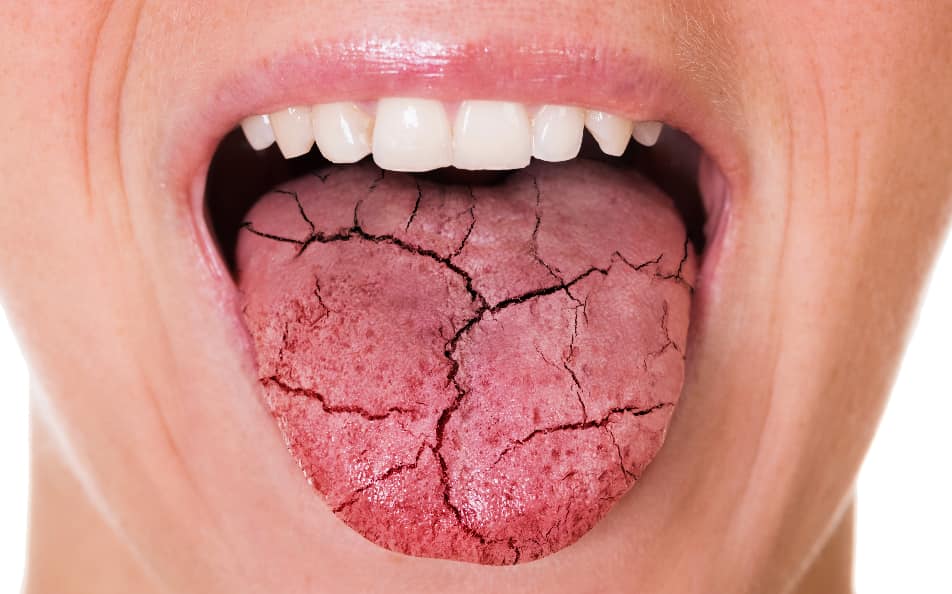
There are different causes of this condition, as noted by the NIDCR, such as dryness due to certain medication, radio, chemo or immunotherapy, diabetes, Sjögren’s, HIV/AIDS, or nerve injury.
Tongue Injury
An injury to the tongue is also believed to cause itchiness. Trauma to the tongue can occur due to an accident or even if you bite down too hard on it. It’s better to get it checked as well as certain injuries can be quite serious.
What Can Help An Itchy Tongue At Home?
As mentioned above, an itchy tongue can be a sign of an anaphylactic shock, which can be life-threatening, so you must get in touch with a medical doctor. In other instances too, you should ask your dentist about any home-management therapies.
For preventing OAS, for instance, one of the things your practitioner might recommend is cooking or peeling foods that trigger a reaction. For instance, according to UpToDate, cooking or heating can help eliminate triggering allergens; as a result, foods that are cooked or canned rarely cause symptoms of oral allergy syndrome. Peeling off the skin of the fruit or vegetable is also believed to help.
For others, such as burning mouth syndrome, some at-home remedies, according to Mayo Clinic, include:
- Drinking plenty of fluids and even chewing on ice chips
- Avoiding foods that might worsen the problem (such as spices, acidic foods, alcohol, etc.)
- Quitting the use of any tobacco products
- Looking for ways to reduce stress
- Using toothpaste that’s not flavoured (as ingredients like mint might aggravate it).
In the case of the herpes virus, you might need medications. Certain dietary changes might also be recommended so the sore doesn’t cause even more discomfort. You also shouldn’t try scratching the sore, as that can only worsen things.

For oral candidosis, according to Verywell Health, at-home remedies may include the use of saltwater rinses and eating probiotic foods (e.g. yoghurt, kimchi sauerkraut), among other things, although, again, the need to get checked by a healthcare professional is emphasised. You also need to maintain good oral hygiene, although you should consider using a clean and soft-bristled brush.
For dry mouth as well, besides keeping hydrated, there are other home remedies outlined by John Hopkins Medicine, including chewing sugarless gum, avoiding caffeine and alcohol, using saliva substitutes, trying a humidifier, etc.
How Can You Make Your Tongue Stop Itching?
To make your tongue stop itching, you need to address the underlying cause of the problem. You must consult a medical professional on this, and they’ll prepare a suitable treatment plan for you.
For OAS, management may include avoiding triggering foods, but to make sure your diet is balanced, it’s best to consult a professional. Antihistamines might be given, but in the case of a severe reaction, you need to get emergency help. In the event of the latter, you may also be prescribed an EpiPen by your doctor.
Angioedema treatment may vary depending on the type you have. You might be advised to avoid any allergens that might trigger an allergic reaction and prescribed medications, such as antihistamines, steroids, epinephrine, etc. It can also need emergency treatment.
The treatment for BMS will first involve identifying the cause (if any). Afterwards, the treatment may involve the use of certain medications, such as antidepressants or even antiseizures. Pain relievers and therapy might also be recommended.
Herpes treatment can also include the use of pain relievers, but since it’s a viral infection, your doctor might also prescribe anti-viral medication. Oral thrush, being a fungal infection, can require treatment with antifungals.
In case your itchy tongue is due to dry mouth, your dentist might recommend products to help keep the mouth lubricated. However, since xerostomia can also be caused by different things, the final treatment plan will depend on the diagnosis of the underlying cause.
Conclusion
An itchy tongue isn’t something that you can easily ignore. Not only can it be discomforting, but depending on what’s making your tongue itch, it can be accompanied by other very discomforting symptoms.
Most importantly, an itchy tongue can be a sign of a severe allergic reaction, in which case you should waste no time in getting medical help immediately. Only a professional medical practitioner can diagnose your problem and prepare the most effective treatment plan for you.
