Taurodontism is a type of dental abnormality that you might not even know you have. It’s a type of condition which results in the enlargement of the tooth’s body at the expense of its roots. The outcome is a tooth resembling that of a bull, hence deriving its name from “tauro,” meaning bull, and “odont,” denoting tooth.
While on the surface, there might not be any problem with the tooth, taurodont teeth can become an issue if you need certain dental procedures. In this guide, you’ll learn more about what taurodontism exactly is, its causes and what can be done about it.
What Is Taurodontism?
In 1908, taurodontism was first described by Gorjanovic-Kramberger in a 70,000-year-old pre-Neanderthal fossil. However, the term itself was coined by Sir Arthur Keith in 1913 to describe teeth that were like that of a bull. Some of the notable features of this kind of tooth include:
- Enlarged pulp chamber
- Bifurcation or trifurcation (division into two or three) of the roots near the apices (tips)
- Apical displacement of the pulp of the floor
- Rectangular-shaped tooth with short roots
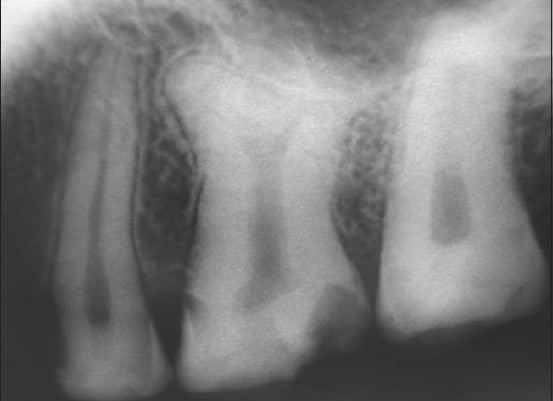
While taurodontism can affect both baby and permanent teeth, it’s more common in the latter, and its prevalence rate varies between 0.5% and 46%, as reported in a 2021 study published in BDJ Open.
One of the bigger issues with these kinds of teeth is that they make it difficult for a patient to get endodontic and orthodontic treatments. For instance, in the case of a root canal, the anatomy of taurodont teeth is more complicated; even the filling of the tooth is not easy.
In the case of orthodontic treatments as well, taurodontism can pose problems. As noted in a study published in the Journal of Dentistry Defence Section, in taurodontism, the surface area of the root is decreased and patients with this condition are advised against wearing orthodontic headgears because the root support is reduced. Additionally, in orthodontic treatments, there’s also a risk of root resorption for such patients.
There are also contradictory reports on its impact on the extraction of teeth. Some say that the dilation of the roots in the apical third would make it difficult to take the tooth out. However, others say that because of how it is, it might not be lodged so well in its place, making extraction easier. Regardless, getting dental treatments may be tricky with these teeth.
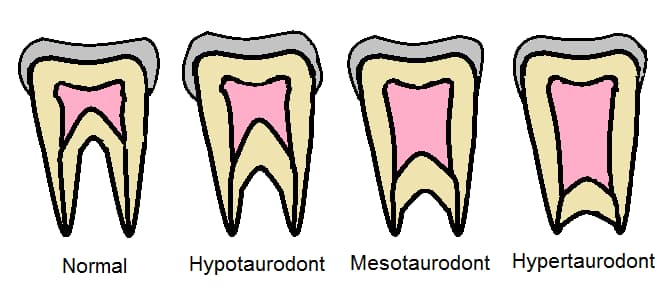
What Are The Three Types Of Taurodontism?
Shaw’s 1928 classification of taurodontism, as per the 2021 study published in BDJ, Open is as follows:
- Hypotaurodontism (mild form) – When the pulp chambers are moderately enlarged.
- Mesotaurodontism (moderate form) – The pulp chamber is relatively enlarged, but the tooth roots are still separated.
- Hypertaurodontism (severe form) – When the pulp chambers have enlarged to the point of nearly reaching the tooth apex and are divided into “conically shaped roots”.
What Causes Taurodontism?
Taurodontism has been associated with many health conditions, such as:
- Down’s syndrome
- Kleinfelter syndrome
- Ectodermal dysplasia
- Amelogenesis imperfecta
- Tricho–dento–osseous syndrome
- Cleft lip and/or palate
- Apert’s syndrome
- Mohr syndrome
- Van der Woude’s syndrome
Usually, it appears as an isolated abnormality, but depending on the condition it is associated with, the symptoms can vary. There may be genetic influence in the development of this condition, yet it’s exact cause is not known.
How Is Taurodontism Diagnosed?
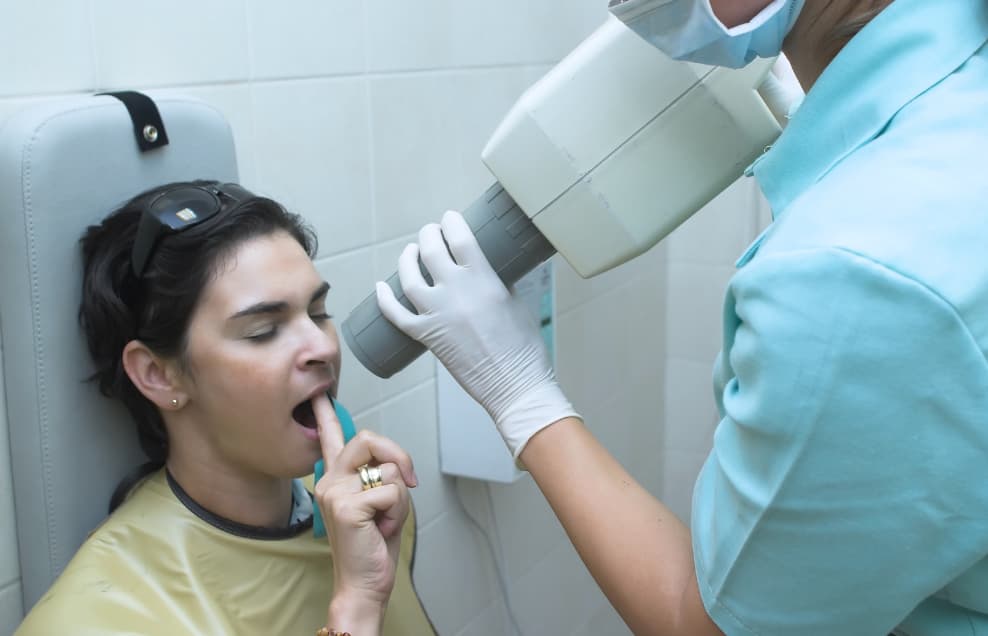
Since taurodontic teeth may appear normal on the surface, dentists have used radiographs or X-rays in the diagnosis of such teeth. However, dental cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) – which can provide a 3D image of the tooth and the tissues around it – has also been reported to help with the diagnostic process. In any case, the goal is for your dentist to understand the structure of your tooth and look for signs of taurodontism.
How Do You Treat Taurodontism?
The treatment for taurodontic teeth will depend on the complications you’re experiencing there. On its own, however, such a tooth might not need any intervention (if it’s not causing any issues). But you must consult a board-certified dentist for the most suitable advice and treatment plan.
Conclusion
Taurodontism is a relatively rare dental problem that impacts the structure of the tooth, prominently the pulp chambers and the roots. While, by themselves, these teeth might not need treatment, in the case of an endodontic and/or orthodontic therapy, things can become more challenging for the dentist.
If you’re experiencing any problem with your oral health, it’s important that you get in touch with a board-certified dental professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan.
Reviewed and approved by Dr Izbel Aksit
