Trench mouth is a severe oral health problem that has been around for more than a century.
According to the European Federation of Periodontology (EFP), the word originates from World War I, when the soldiers in trenches suffered from this oral health problem due to poor oral hygiene.
Unfortunately, “trench mouth” is extremely destructive, so early treatment is crucial to preventing irreparable damage.
For that, you need to be aware of its various signs and symptoms. And to help prevent trench mouth, you should first understand its risk factors; this will help you avoid acquiring this condition.
What Is Trench Mouth?
A trench mouth is a rare, painful infection of the gums that causes ulceration and inflammation. It is a more serious form of gum disease and can spread quite rapidly.
More commonly, this condition affects people between the ages of 15 and 35. Also, it is more prevalent in developing countries, where it more commonly affects children.
However, adults are also vulnerable to this if certain predisposing factors are present. Trench mouth is also known by many other names, such as:
- Acute Necrotising Ulcerative Gingivitis (ANUG)
- Acute Membranous Gingivitis
- Vincent’s Angina
- Vincent’s Infection
- Vincent’s Gingivitis
- Vincennes Disease
- Phagedenic Gingivitis
- Fusospirochetal Gingivitis
- Fusospirillosis
Bear in mind that trench mouth is a result of the imbalance of microbial flora. It occurs due to the overgrowth of the bacteria in the mouth that’s normally present. Mainly, fusiform bacteria and spirochetes are responsible for this condition.
It should be noted that trench mouth or acute necrotising ulcerative gingivitis can progress to a more serious condition called acute necrotising ulcerative periodontitis (ANUP).
While the former only affects the gums, the latter can cause clinical attachment loss and even spread to the alveolar bone.
It can also be fatal if it ends up necrotising the soft and hard tissues in the oral cavity. This is known as noma or cancrum oris. and it can cause severe disfigurement.
What Causes Trench Mouth?
It is believed that trench mouth is caused by malnutrition, poor oral hygiene, and psychological stress. However, there are other risk factors, such as:
- Preexisting gingivitis
- Smoking
- Trauma
- Consumption of tobacco products
- Alcohol abuse
- Trauma
- Living near livestock
According to the European Federation of Periodontology, soldiers in the Great War preferred receiving “sugar-packed fruitcake” in parcels over “tooth powder or brushes.”
Unfortunately, the conditions didn’t allow them to maintain their oral hygiene.
In addition to that, they were under immense stress and were not getting adequate nutrition. Together, these factors contributed to the prevalence of this condition during that time.
And because it affected the soldiers in the trenches, that’s where the name of this condition came from.
Since the risk factors for trench mouth are still present, people with lower socioeconomic status are particularly vulnerable to it still.
The bacteria responsible for it is already present in the mouth, so when the conditions are ripe for them to flourish, they do so.
Here, it should be noted that immuno-compromised individuals are more susceptible to this condition.
Trench mouth may be more common in people who have diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or cancer (or are undergoing cancer treatment). The same goes for those who’re taking immunosuppressants (usually following an organ transplant).
What Are Symptoms Of Trench Mouth?
A trench mouth is an infection that can destroy the tissue in the mouth permanently. It necrotises them, which means that they die.
And this tissue degradation can result in a foetid odour. An extremely foul breath is usually taken as the first sign of ANUG. But it also has other symptoms, which include:
- Ulceration (like craters or punched-out areas between teeth)
- Sloughing off of dead cells in the mouth
- Swelling
- Feeling of tightness around teeth (in initial stages)
- Severe pain
- Metallic taste in the mouth
- Bleeding
- Grey film on gum tissue
- Swelling of the lymph nodes (lymphadenopathy)
- Fever
- General malaise
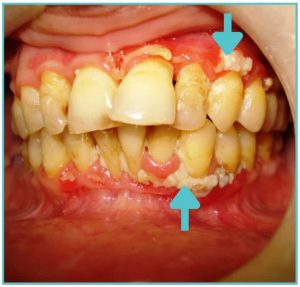
Here, it should be noted that trench mouth can also cause weight loss and dehydration. That’s because the pain can be so intense that a person can find it difficult to eat or drink anything.
They can’t even brush their teeth. A simple touch can result in pain. Initially, this pain will be limited to the affected area, but once the lesion spreads, it can be experienced in the entire mouth.
Other than that, there’s also the risk of tooth loss. If that occurs, you’ll end up requiring restorative treatments like crowns, bridges, or implants. Bear in mind that this infection can spread to other areas of the body and be fatal.
How To Treat Trench Mouth?
Antibiotics can quickly and easily treat trench mouth. However, other treatments may be needed depending on the severity of the problem. For that, the dentist will perform a thorough physical examination.
An X-ray may be needed to check for any damage to the structures beneath the gum tissue. A blood test may also be needed to check if the infection has spread to other parts of the body, along with a throat swab.
After the confirmation of the diagnosis, the treatment plan is devised. Usually, the consists of the following steps:
- Stopping the infection and relieving pain
- Treating the underlying problem
- Restoring gum tissue damaged by the infection
Antibiotics like penicillin, tetracyclines, metronidazole, and amoxicillin are prescribed for clearing up the infection. Painkillers are also recommended for relief.
Other than that, saltwater rinses (half a teaspoon of salt in 1 cup of water), hydrogen peroxide and chlorhexidine mouthwashes can further help.
Keep in mind that you should not do anything on your own without consulting a medical professional. You may end up worsening your problem.
Once your gums feel a little better, you may need a cleaning appointment. If it still hurts, your dentist will likely numb the area beforehand.
Your gums may also need reshaping or regeneration to cover the punched-out areas. Necrosis tissue may also require surgical treatment.
While you’re undergoing treatment, you should refrain from smoking or eating foods that are hot and spicy.
Usually, the entire treatment lasts for a few weeks, but you’ll start feeling better.
However, keep in mind that a trench mouth will not heal on its own; you need treatment and the earlier, the better.
How To Prevent Trench Mouth?
It may be possible to prevent a trench mouth by doing the following:
- Good oral hygiene – You need to make sure that you’re brushing your teeth the right way, flossing and using mouthwash to keep your mouth clean and healthy.
- Eating healthy foods – Poor nutrition can lead to tooth decay, which is why you need to make sure that you’re eating well. It’s also important to not consume too many sugary foods as that too can damage your teeth.
- Coping with stress – Stress itself is normal, but you should know how to deal with it as it can be a risk factor for trench mouth. Exercising, meditation, mindfulness, and talking to others can help.
- Getting adequate sleep – You need to sleep for at least 8 hours every night. That’s because sleeping can help reduce cortisol (stress hormone) levels. It can help reduce stress and improve your mood and energy levels.
- Getting regular checkups – If you have a trench mouth, early treatment can prevent extensive damage to your mouth. And it’s possible to detect it in its early stages if you’re getting a regular checkup and professional cleaning.
- Refraining from smoking – Smoking is injurious to your health in countless ways. It’s also a risk factor for ANUG, which is why you need to quit it.
If you have an underlying health problem that affects your immune system, consult your doctor for more information on how to prevent this infection.
Conclusion
Trench mouth or acute necrotising ulcerative gingivitis is a serious infection of the gums that can cause permanent damage.
There are different factors that cause it, such as poor oral health, stress, and malnutrition. Since these risk factors can be taken care of, it is possible to reduce the risk of this infection.
However, if you have developed it, it’s important to get treatment as early as possible. The lesions in your mouth can spread, and the infection can start affecting other areas of the mouth.
It can even spread to your body and can even cause death. Therefore, if you notice that something’s not right with your mouth, get in touch with your dentist immediately.
