One of the most common oral health problems is gum disease. It’s the infection of the gum tissues surrounding the teeth due to plaque accumulation.
In fact, it should be noted that “gum disease” is something of a misnomer. This is because gum disease can also affect the jawbone, cementum (tissue covering the tooth root), and periodontal ligament (tissue connecting the tooth to the jawbone).
Research has also indicated its association with more serious health problems affecting the heart, among other organs. And while certain factors can increase the risk of gum disease, this condition is largely preventable.
Even if you’ve developed it, it’s possible to reverse it in its early stages. But if left untreated, it can cause irreversible damage, which will be far more expensive to treat.
What’s Gum Disease Exactly?
A gum (periodontal) disease is a disease affecting the structures surrounding and supporting a tooth.
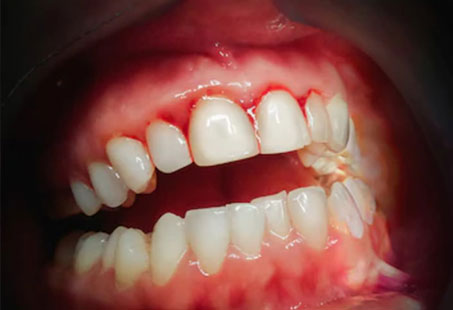
According to the NHS, gum disease affects most adults in the UK to an extent. And it’s so common that most people experience it at least once in their lifetime.
And while it can affect people of many different ethnicities, it tends to be more prevalent in African Americans.
Also, according to a study published in the American Journal of Men’s Health, men are more likely to have it due to relatively poor oral hygiene, greater tobacco use and immune and hormone differences.
Socioeconomic factors are also at play here. When income and education levels are low, gum disease is more prevalent. There are other disparities in access to oral healthcare, which make this disease more common in some people than others.
And unfortunately, many different researchers have found a link between gum disease and serious health problems.
Gum Disease and Other Diseases
Following are the diseases which have been associated with gum disease:
Heart Disease
It’s believed that the inflammation caused by gum disease can increase the risk of heart problems
Moreover, bacteria that cause gum disease can enter the bloodstream and cause infection of heart valves. It’s also suspected that gum disease can worsen an existing heart problem.
Neurological Problems
One study published in Science Advances that gum disease bacteria can kill neurons in the brain and induce other changes associated with Alzheimer’s.
Brain inflammation caused by gum disease is also associated with dementia. And people with dementia are also less likely to have good oral hygiene, which further increases their risk of gum disease.
Other than that, the American Heart Association also reports that people with gum disease are twice as likely to suffer a stroke due to the hardening of large arteries inside the brain.
Respiratory Diseases
Oral health affects lung health as well.
And if you have periodontal disease, research shows that the bacteria in your mouth can influence the development of respiratory infections (like pneumonia) and lung inflammation.
Research published in the Journal of Periodontology also found that gum disease increases the risk of lung cancer.
Unfortunately, it’s not the only cancer that gum disease increases the risk of. Periodontal disease can also increase the risk of blood, kidney and pancreatic cancers.
Birth Problems
Your oral health can also affect the health of your unborn child.
Research shows that gum disease is associated with premature birth and low birth weight.
While understandably, you might be hesitant to have a dental procedure while pregnant, if you are experiencing an oral health problem, you should get yourself checked.
This is especially important because hormonal changes during pregnancy cause inflammation, which, in turn, leads to gum disease.
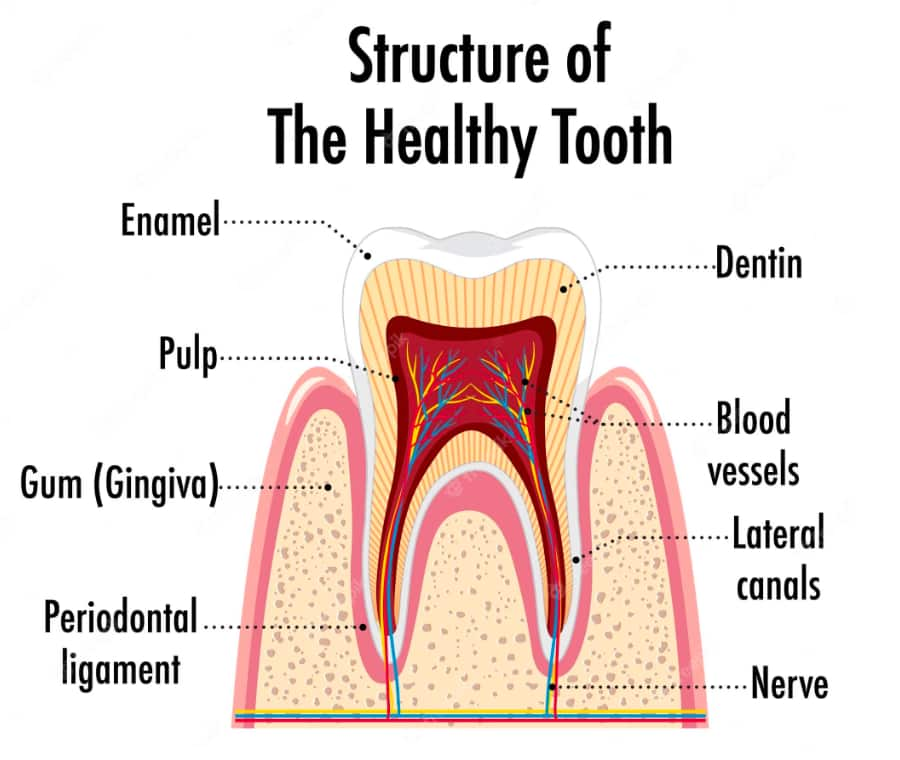
What Are The Stages Of Gum Disease?
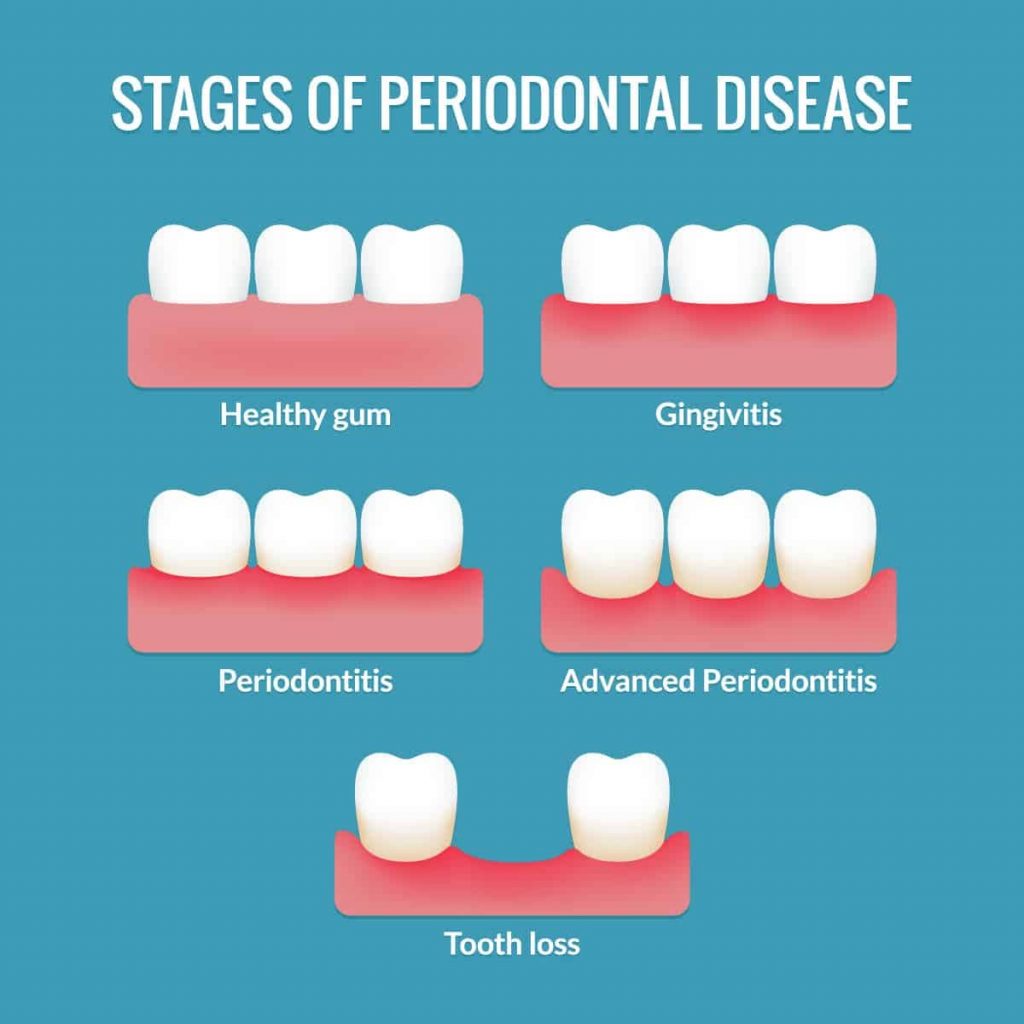
Mainly there are two stages of gum disease: gingivitis and periodontitis. They differ primarily in severity and reversibility.
Gingivitis is milder, reversible, and only affects the gums. However, periodontitis is far more severe, irreversible and affects tissues below the gums as well. Let’s take a closer look at each of them:
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gum tissue. It’s the first stage of gum disease and usually doesn’t cause a lot of problems.
Signs that you have gingivitis include:
- Red and swollen gums
- Bleeding gums (on their own and especially when brushing or eating)
It’s even possible for gingivitis to be asymptomatic. Therefore, it can go unnoticed for quite some time.
And in that case, it can progress to more serious peridontitis (although it doesn’t always happen).
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is when the gum infection spreads to the deeper structures surrounding the tooth. This includes the jawbone, cementum, and the periodontal ligament.
At this stage, the gums start to recede, and as they pull away, the teeth start to look longer than usual. Eventually, it can even expose the tooth roots, which can be very painful.
Other than that, gum recession also forms “periodontal pockets” around the tooth. With these present, it becomes even easier for bacteria to get trapped around the teeth, causing more damage.
Meanwhile, your jawbone will continue to deteriorate, which will start making your teeth shift. They’ll also become loose because they’re not strongly anchored anymore. This can even lead you to lose your tooth entirely.
The damage from the bacterial toxins aside, the body’s inflammatory response to them will also damage the tissues beneath the gums.
There’s even a “necrotising periodontitis” that destroys both the gums and jawbone irreversibly. Necrosis means the death of body tissue.
What Are The Symptoms Of Gum Disease?
Gum disease symptoms are as follows:
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Redness
- Pain
- Bad breath
- Bleeding
- Gum abscess
- Dark gums
- Gum recession
- Sensitivity to hot and cold foods
- Loose teeth
- Tooth loss
- Bite or denture fit change
Of course, the symptoms can vary depending on how severe your gum disease is. You might not always notice them in time, which is why you should get regular dental checkups.
How Do You Know If You Have Gum Disease?
When it comes to gum disease, you should mainly look out for any signs of inflammation (redness, swelling, pain, etc.).
You can check your gums at home yourself by using a mirror. However, it’s always better to consult a medical professional.
What Causes Gum Disease?
Gum disease is caused by the accumulation of plaque. It’s the sticky, colourless film of bacteria that everyone has on their teeth.
And while this film is produced every day, it should also be dislodged every day by brushing so it doesn’t build up and harden into tartar, also known as calculus.
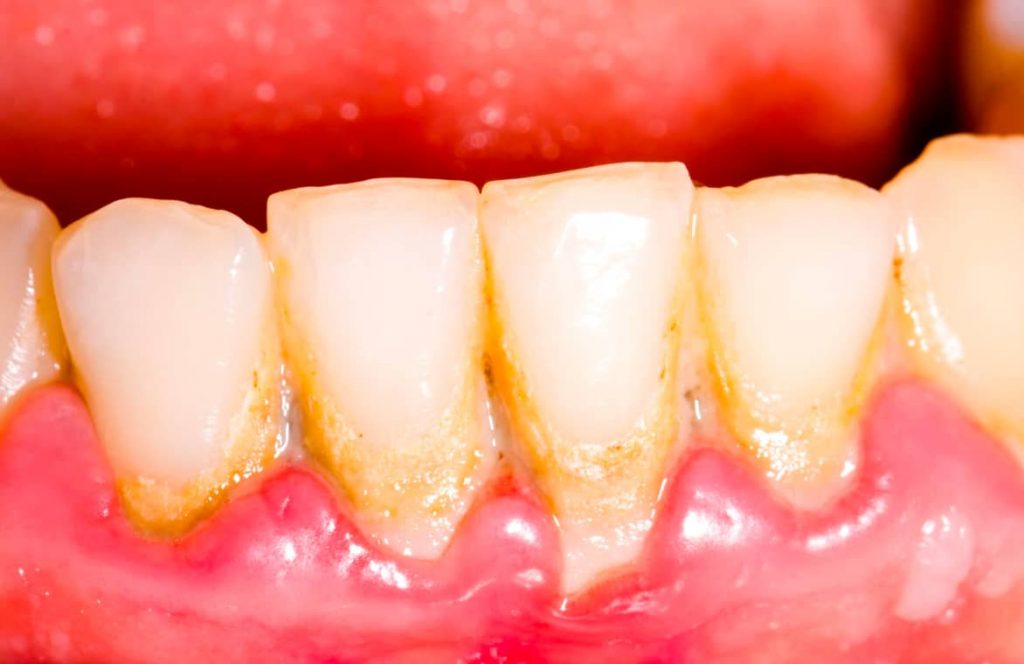
The bacteria in the plaque release acids that can break down the enamel. But this plaque doesn’t just stay on the visible part of the tooth.
It can go deep down and damage the jawbone as well, which is what happens in the more severe form of gum disease. And that’s the answer to how do you get gum disease.
Here, it’s important to note that you might be more likely to get gum disease due to the following factors:
- Old age – Gum recession in old age can make plaque accumulation easier. Inflammation is also more severe. Moreover, it becomes harder to maintain good oral hygiene.
- Family history – Your genetics can also increase the risk of gum disease by 6 times.
- Misaligned teeth – If your teeth are crooked or wonky, they’ll be harder to clean, allowing plaque to accumulate.
- Poor oral hygiene – If you don’t brush or floss to dislodge the plaque, the bacteria will damage your teeth, gums, and bone.
- Bruxism – Clenching and grinding your teeth may not cause gum disease, but it can worsen it.
- Bad diet – Bacteria use sugar from your food and form plaque. So, if your diet is high in sugar, you’re increasing the risk of gum disease. Too much alcohol and too less water are additional risk factors.
- Tobacco – It affects healing and the oral microbiome, both of which can promote gum disease. According to the CDC, smokers are twice as likely to get gum disease. Even gum disease treatments might not be as effective in smokers. Also, research shows an association between vaping and gum disease.
- Health problems – Diabetes, HIV, Crohn’s, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, obesity, Down syndrome, and Sjögren’s are some of the health problems that increase the risk of gum disease.
- Medications – Chemotherapy drugs, calcium channel blockers, steroids, oral contraceptives and anti-epileptic drugs are also risk factors for gum disease.
- Hormones – Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy, menopause, or even puberty can also lead to gingivitis and periodontitis.
- Stress – It affects your immunity and can make you less careful about your oral hygiene.
All these are risk factors for gum disease.
How To Treat Gum Disease?
The gum disease treatment depends on the severity of the problem.
For instance, if you have gingivitis, good oral care can make a significant difference. However, patients usually require cleaning of their teeth. And for that, scaling and root planing are done.
These are deep cleaning procedures that clean out the bacteria above and below the gum line. Scaling scrapes the tooth surface, while root planing cleans and smooths out the tooth roots so they can reattach.
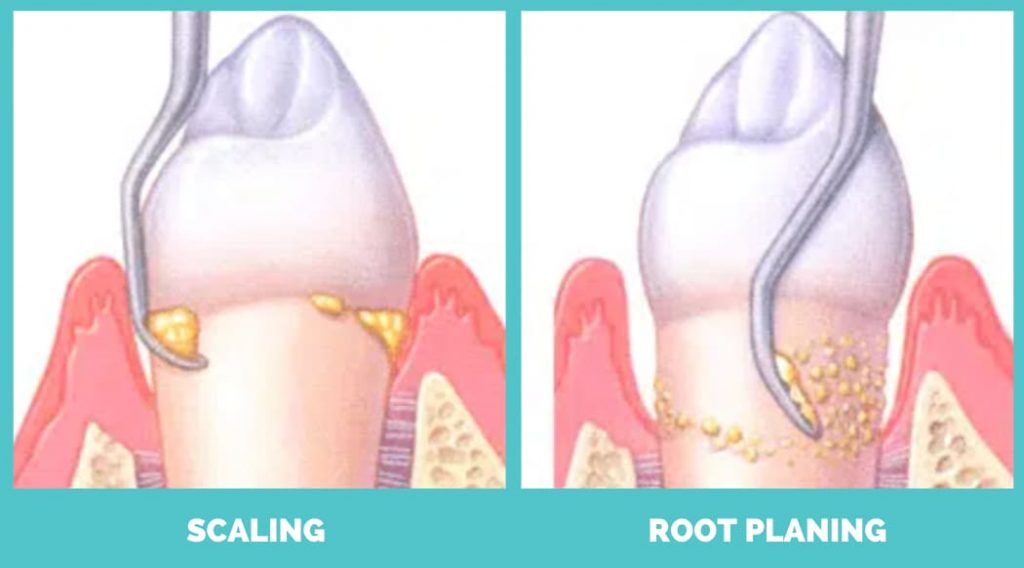
Your teeth might feel a bit loose after these procedures. That’s because your teeth were supported by the tartar before it was removed. Of course, that’s not healthy, and it has to be cleaned to allow the gums to heal.
Other than scaling and root planing, your dentist might recommend periodontal flap surgery if the pockets around the teeth are very deep. For this, the gum tissue is cut so that the tooth roots can be clearly seen and cleaned out.
However, the answer to how is gum disease treated depends on the condition of your teeth, gums and bone.
If the tooth is too far gone and badly damaged, your dentist might recommend extracting the tooth instead.
And to improve the overall health of your mouth, you might need additional procedures like bone grafting (due to jawbone loss), gum grafting (due to gum recession), and dental implants Turkey with dentures or crowns.
In-office treatments can also be combined with medications like antibiotics, painkillers, and antiseptic mouthwash.
Make sure to consult a qualified and board-certified dentist for the best treatment for gum disease. They’ll chalk up a treatment plan for you on how to fix gum disease.
Can Gum Disease Be Cured?
Gingivitis can be cured, but periodontitis isn’t curable. Even if you have gingivitis, it’s important to seek early treatment.
According to StatPearls, gingivitis can be reversed within 7 to 10 days if good oral hygiene is practised. That’s one answer to how to get rid of gum disease.
However, the same cannot be said for periodontitis. For that, the answer to how to cure gum disease is that it’s not possible. You can seek treatment to manage and control it, but this gum disease cure is not available.
And as you’re getting treatment, it’s also important for you to avoid risk factors (which can be avoided) and take good care of your teeth.
How Much Does Gum Disease Treatment Cost?
The gum disease treatment cost will depend on the kind of treatment you’re getting. That, of course, depends on the extent of your problem.
You can get clinically necessary treatments on the NHS. However, long wait times may be an issue there, during which the condition of your oral health can worsen.
You can consider getting treatment at a private clinic, but that can cost more. If it’s just scaling and root planing, however, it usually costs £100 or so. Consultation and follow-up can cost you a few more hundred pounds.
But if it’s a more invasive flap, bone grafting, gum grafting and/or implant procedure (with restorations), it can cost you tens of thousands.
If you’re looking to save costs, you can consider becoming a medical tourist in Turkey. Prices at dental clinics in Turkey are 3-5 times less than in the UK.
How Long Does Gum Disease Last?
Gum disease can last for as long as it’s left untreated. It won’t reverse, stop or slow down unless you take the necessary steps to protect your teeth and gums.
The progression can also be slow and fast. And it can occur in episodes of active tissue followed by a period of dormancy and recovery.
But if it’s peridontitis, it won’t go away on its own because it’s not curable. Even when it’s mild, you have to change your dental hygiene routine to restore your gum health.
What Helps Gum Disease?
You can help your gum disease by doing the following:
- Brush & floss – Use a soft-bristled brush with fluoride toothpaste to clean your teeth twice a day (each round at least 2 minutes). Also, floss at least once a day.
- Mouthwash – It can be a beneficial addition to your dental routine and help you keep your mouth clean.
- Quit smoking – Seeing how smoking can harm your oral (and overall) health, it’s a good idea to quit it altogether.
- Eat & drink healthily – It’s important to cut down on foods that are too sugary and acidic, especially if you have diabetes. You should also drink a lot of water to keep your mouth clean.
- Live healthily – Stress is a part of life, but you should look for ways to manage it so it doesn’t have a very negative effect on your oral health. Adequate sleep, exercise, meditation, deep breathing, etc. can help.
- Clean dentures – Denture hygiene is important to not allow any plaque build-up in your mouth.
- Get teeth straightened – If you have misalignment, you can benefit from braces or dental restorations. With straighter teeth, cleanliness and oral hygiene can be easier.
- Get regular checkups – Visit your dentist every 6 months to make sure that your gum disease is under control or managed just in time.
And if you’re wondering how to prevent gum disease, these measures can help you with that as well.
Keep in mind that gum disease won’t just affect your gums, so it’s important to be very careful. Don’t wait if you already have signs of gum disease. Get in touch with your dentist immediately.
Reviewed and approved by Dr Izbel Aksit
FAQ
What does gum disease look like?
Inflammation is the main sign of gum disease. It can cause swelling, pain, and redness. You should also look out for any change in the colour of your gums (they get darker).
Can gum disease kill you?
Severe gum disease has been associated with serious health problems that can be fatal, such as a stroke, Alzheimer’s and pneumonia.
Is gum disease contagious?
It is possible to transmit gum disease bacteria through saliva exchange, which can lead to gum disease, especially if the other person is unwell.
Can you catch gum disease?
Depending on your health, it may be possible for you to catch gum disease from someone else through saliva exchange. However, in families, genetics can also play a role in this.
Is gum disease common?
Gum disease is very common. In fact, it’s the most common oral disease. According to StatPearls, it affects about 90% of the population worldwide.
What is the quickest way to get rid of gum disease?
How quickly you can get rid of gum disease may depend on its severity, your health and lifestyle. You can practise good oral hygiene, but make sure to seek the help of a professional.
How to stop gum disease?
Getting early treatment is important in stopping, slowing down or even reversing gum disease. Additionally, you need to have a good oral hygiene routine.