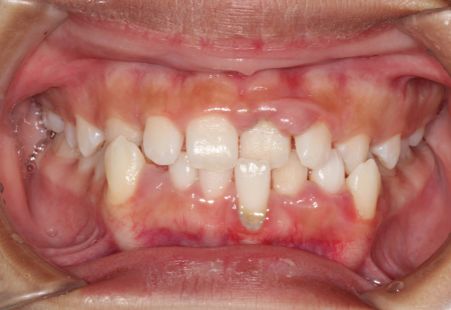
Different oral health problems can be symptomatic of other health conditions. Gingival hyperplasia or gum tissue overgrowth can be caused by a number of factors. It can cause functional and aesthetic problems, which is why many people seek treatments for it.
It should be noted that gingival hyperplasia can be a recurrent condition. If the underlying problem is treated, it can disappear. However, it can return. In some cases, the condition is permanent and is present from birth.
What Is Gingival Hyperplasia?
Gingival hyperplasia, also known as gingival hypertrophy, is the overgrowth of the gum tissue around the teeth (front, back, in between). It can appear as a protruded bump. The severity of the condition can vary, but, in some cases, it can cover as much as the entire tooth. It can expand in all directions and affect more than one tooth:
- Localised Gingival Hyperplasia – The gum tissue is overgrown on a group of teeth; the location is confined.
- Generalised Gingival Hyperplasia – The gum tissue in the entire mouth is affected.
Depending on the cause of the enlargement, the gum is thickened, soft or firm, and pale pink or dark purple in colour. It is also possible that barely any of the teeth are visible from beneath the gums. According to the American Academy of Oral Medicine, this condition is not contagious. You cannot catch it from someone or pass it on.
What Are the Symptoms of Gingival Hyperplasia?
Other than the obvious enlargement of the gum tissue, you might also experience the following:
- Easily bleeding gums
- Tenderness
- Pain
- Discomfort
- Bad breath (halitosis) due to entrapment of food
- Teeth misalignment
- Difficulty chewing and talking
- Hindrance in the eruption of a new tooth
Keep in mind that no matter what, you should always consult a professional dentist and get an accurate diagnosis from them of your problem. If you’re experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, you should immediately get in touch with your dentist to prevent the worsening of the condition.
What Can Cause Gingival Hyperplasia?
You can develop this condition because of the following reasons:
Inflammation
Both acute and chronic inflammation can result in gum enlargement. It can have different causes, such as gum disease (gingivitis or periodontitis) or improperly fitting dental appliances (dentures, braces).
Chronic gum inflammation can also be caused by a rare condition known as Papillon-Lefèvre syndrome. It can also cause an overgrowth of the gum tissue. Inflammation can develop as a result of the formation of plaque around the teeth. People who smoke or breathe through their mouths are at a higher risk. If these health problems are taken care of in time, gingival hyperplasia can be resolved.
Drug-Induced
Gingival hyperplasia is also a side effect of certain medications. It can develop a few months after their intake. This problem is most often caused by:
- Anticonvulsants
- Immunosuppressants (for autoimmune disorders and preventing organ transplant rejection)
- Calcium channel blockers (for cardiovascular conditions)
According to a study published in the Mayo Clinic Proceedings, phenytoin (most common anticonvulsant), cyclosporine (most common immunosuppressant), or calcium channel blockers will result in some degree of gingival hyperplasia in 40-50% of the patients.
Research shows that a combination of cyclosporine and calcium channel blockers can result in aggravation of the problem. Rarely, this condition can be a result of the intake of antibiotics, antidepressants, or other medications. If you’re wondering what drugs cause gingival hyperplasia, here’s a list:
| Anticonvulsants | Immunosuppressants | Calcium channel blockers |
| Phenytoin | Cyclosporine | Nifedipine |
| Vigabatrin | Tacrolimus | Felodipine |
| Primidone | Sirolimus | Amlodipine |
| Mephenytoin | Methotrexate | Nitrendipine |
| Ethosuximide | Diltiazem | |
| Phenobarbital | Verapamil |
Even when it comes to drug-induced gingival hyperplasia, the formation of plaque in the mouth may be behind the problem. That is why it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene. Your doctor may recommend the use of the antiseptic chlorhexidine mouthwash. In addition, you should make sure to get regular dental cleanings to reduce the risk of this condition.
Family History
Gingival hyperplasia can also run in families because of the involvement of the genes. It could be a result of the following:
- Idiopathic gum overgrowth (cause of the problem is unknown)
- Storage disorders (problems with metabolism)
- Circulatory system diseases
- Dental anomalies
As far as idiopathic or hereditary gingival fibromatosis is concerned, it can start developing from an early age, but you may notice it in adulthood. The gums may have a pale pink colour and appear granular or like “pebbles.” Other genetic diseases in which this condition can be seen include Sturge-Weber syndrome, Cowden syndrome, Anderson–Fabry disease, etc.
Systemic Conditions
These are the causes that affect the entire body. Once the underlying issue is resolved, gingival hyperplasia should also go away. Keep in mind that not every systemic condition is a health problem.
For instance, you can experience gum enlargement during pregnancy or puberty, which involves fluctuations in hormones. Other health conditions that can result in gingival enlargement include:
- Leukaemia
- Diabetes
- HIV
- Vitamin C deficiency
- Anaemia
- Tuberculosis
- Lymphoma
- Chronic granulomatous diseases (Sarcoidosis, Crohn’s, Amyloidosis, etc.)
Others
There are some other reasons why gum enlargement occurs. It could be due to the formation of a tumour on the gum tissue. It can also swell up as a result of an abscess. Sometimes, there are also “false enlargements,” in which the gum tissue appears enlarged as a result of the problem with the underlying bony tissue or impending eruption of teeth.
How Is Gingival Hyperplasia Diagnosed?
Since there are varied causes of this condition, you need to consult a dental professional. They may ask you about your medical history (any genetic conditions) and medications for any treatments that you’re on. In addition, they will perform a physical exam to find out how well you maintain your oral hygiene or if you’re suffering from any disease.
For an accurate diagnosis, you might also need to have some blood tests done in case it’s a blood-borne problem. Your dentist may also take a small piece of tissue from the gum in what’s known as a biopsy. A mouth culture may also be needed to rule out any infections.
How To Treat Gingival Hyperplasia?
Depending on the root cause of the problem, you may be recommended to undergo one or more of the following treatments.
Scaling & Root Planing
If the plaque has hardened, you may need a scaling treatment. Using a metal hook, the dentist tries removing the plaque above and below the gumline.
However, if the gum pockets are deep and the plaque extends to the root of the tooth, root planing is also needed. These restorative dental procedures will help prevent gum disease from spreading and resolve the issue of gum enlargement.
Gingivectomy
This is the procedure in which the dentist will cut off the excess gum tissue either using a scalpel, laser or electricity.
Laser Excision
An Nd:YAG or CO2 laser is usually used for this purpose. The tip of the laser is pointed at the gum tissue, which then cuts it. It can also be used for the coagulation of the blood, that can help seal off the wound. Following the removal of the gum tissue, the dentist will also scrape off any existing plaque build-up.
Electrosurgery
Instead of a laser tip, the tip of an electrode is used for making the incisions. The electrical currents will cut the soft overgrown tissues of the gums. This surgery allows for greater precision. Plaque removal follows this procedure.
Gingival Flap Surgery
In case the plaque is lodged deep into the gum tissue, so much so that scaling and root planing cannot help, you might need to undergo gingival flap surgery. The surgery mostly takes place under local anaesthesia. The dentist will cut off a flap of the gum tissue to expose the underlying tooth that needs to be cleaned. If you’ve also experienced bone loss, you may be recommended a bone graft surgery along with it.
Change In Medications
As mentioned before, one kind of hyperplasia is caused due to the intake of certain drugs. That does not in any way mean that you should stop taking your medications without consulting your doctor or even switch them to different ones. If you are taking any of the medications above, you should discuss their potential side effects with your doctor.
Although if you’re already experiencing it, you should tell your doctor about it. It is possible that they’ll decrease the dosage or change to another medicine. For instance, research has shown that the incidence of gum enlargement decreases by 65% if the patient is on tacrolimus therapy instead of cyclosporine.
Concluding Remarks
Gingival hyperplasia can disrupt the normal functioning of the mouth. You’ll find it hard to eat certain foods and even talk normally. In addition, the patients can be psychologically affected and find themselves unattractive. That is why many people seek different treatments for it. However, before that, there’s a need to understand the various causes of this condition.
In some cases, the resolution of those problems should be enough to rid you of gum enlargement, but that’s not always possible. In any case, make sure to get examined by a professional, licensed dentist for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan